PRODUCTS CATEGORY

Manganese ore processing line
Manganese is widely distributed in nature, commonly found in anhydrous and hydrated manganese oxides and carbonates.

- Product Description
-
- Commodity name: Manganese ore processing line
Manganese is widely distributed in nature, commonly found in anhydrous and hydrated manganese oxides and carbonates.
Manganese is widely distributed in nature, commonly found in anhydrous and hydrated manganese oxides and carbonates. There are currently 150 known manganese minerals, but there are not many with high manganese content that can be enriched in large quantities to form economically valuable minerals, mainly including pyroxene, pyroxene, and rhodochrosite. The manganese content in these minerals can reach about 50-70%, making them important industrial minerals for manganese. In industry, soft manganese ore with high manganese content is mainly used. Manganese ore processing includes four processes: crushing and screening, dry throwing, grinding, and beneficiation, ultimately producing refined manganese powder.
Technological Process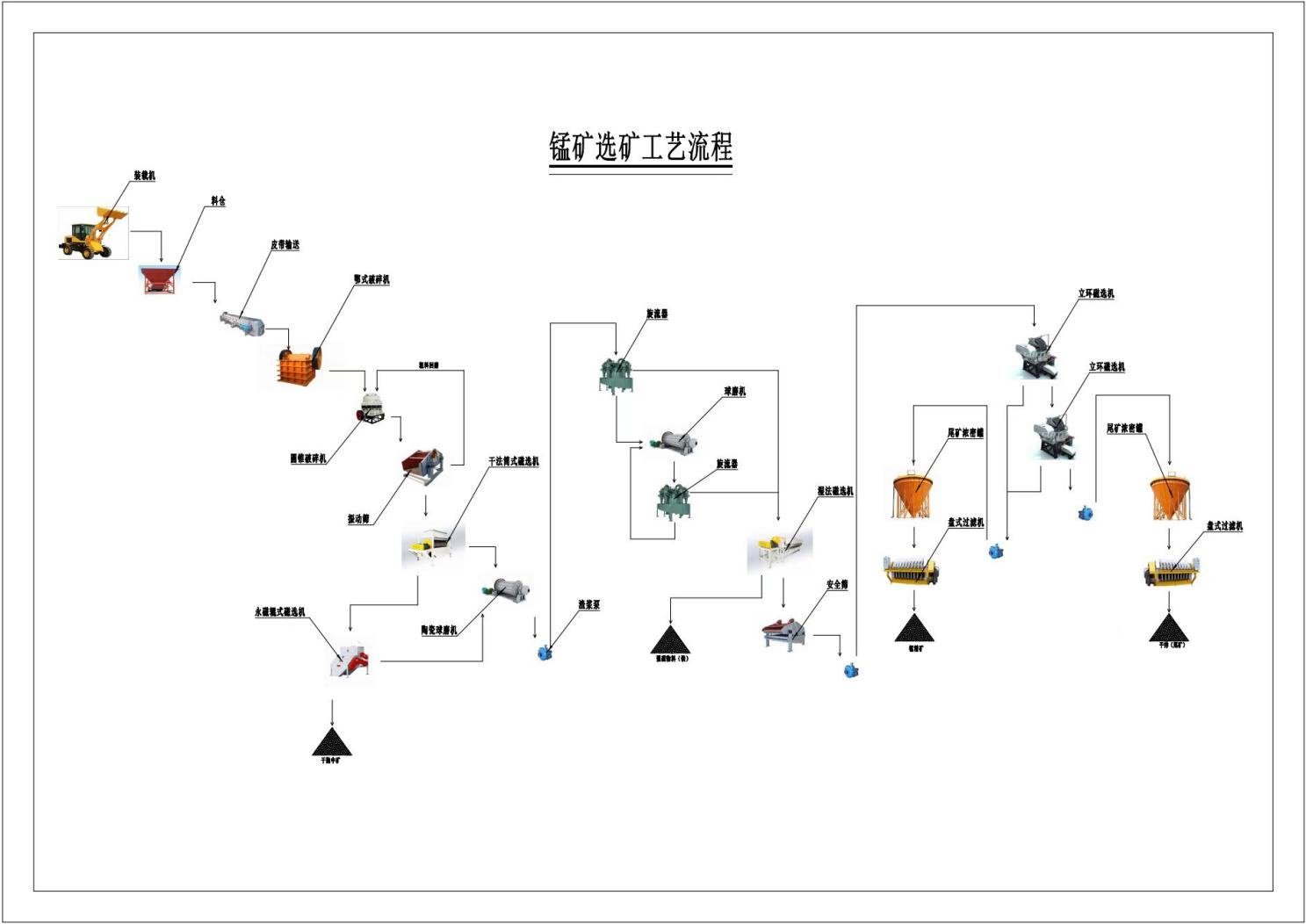
Phase 1: Crushing and screening
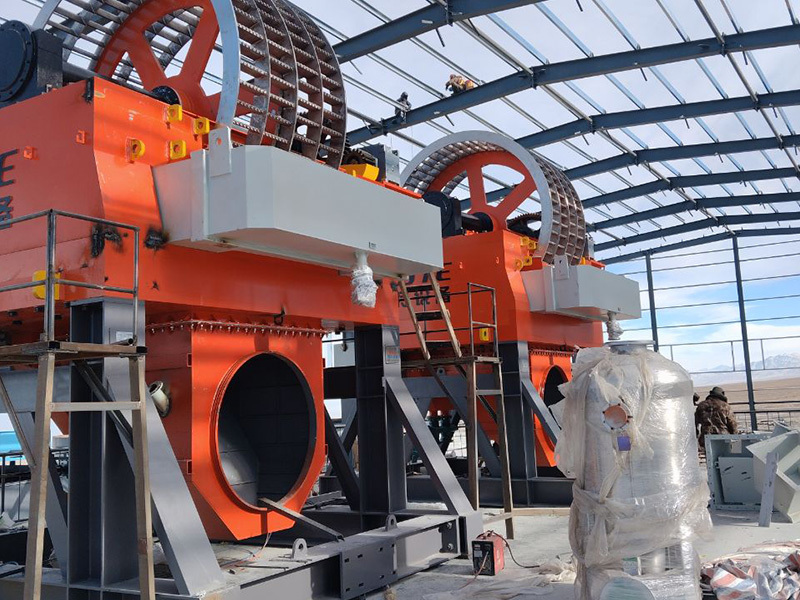
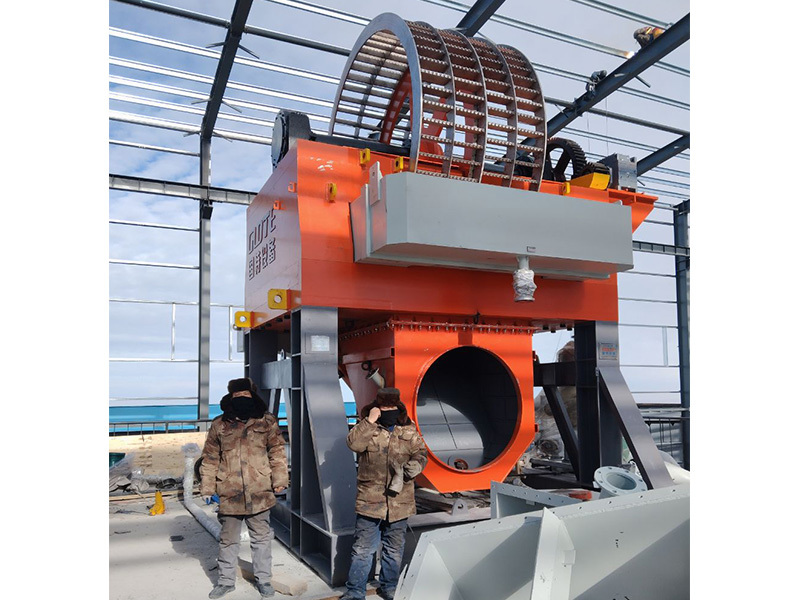
The large manganese ore is uniformly fed into the jaw crusher for coarse crushing by a vibrating feeder through the material bin; After coarse crushing, the manganese ore is sieved by a vibrating screen and then transported by a belt conveyor to a single cylinder hydraulic cone crusher for intermediate crushing; The manganese ore after intermediate crushing is sent to a multi cylinder hydraulic cone crusher for fine crushing.
Phase 2: Dry throwing
The crushed manganese ore is sent to a permanent magnet drum magnetic separator for preliminary magnetic separation. The tailings are discarded, and the concentrate enters a permanent magnet high field strength roller magnetic separator for secondary magnetic separation. The tailings are discarded, and the concentrate enters the next section.
Phase 3: Grinding
After dry throwing, the manganese ore is evenly fed into the mill for grinding, and then the slurry is pumped into a cyclone for coarse and fine separation by a slurry pump. The fine material overflows and enters the next process, while the coarse material enters the second stage mill. After being ground by the second stage mill, it enters the second stage cyclone for coarse and fine separation. Similarly, the fine material enters the next process, and the coarse material returns to the second stage mill, forming a closed-loop cycle.
Phase Four: Mineral Processing
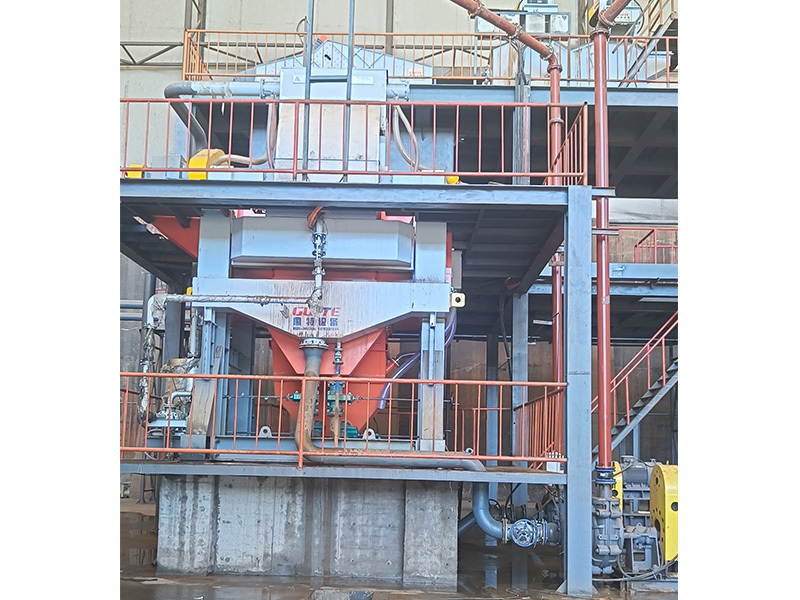
The manganese ore powder with the required particle size is sent to a wet permanent magnet magnetic separator for intermediate magnetic separation to remove mechanical iron from the slurry, and then enters a vibrating safety screen to prevent large materials from entering the next section. Then, the slurry is sent to a high gradient vertical ring magnetic separator for strong magnetic scanning, separating the manganese ore powder from the tailings to obtain manganese concentrate slurry, which is sent to a manganese ore thickening tank. The tailings then enter a two-stage high gradient vertical ring magnetic separator for secondary strong magnetic scanning to obtain scanned manganese concentrate slurry. The manganese concentrate slurry is also sent to a thickening tank for preliminary concentration and dehydration, and then enters a disc filter to achieve separation of concentrate and water. The dehydrated manganese concentrate slurry is transported to a finished product warehouse; The tailings after scanning and selection enter the tailings thickening tank, and after concentration, they enter the disc filter for mud and water separation. The filter dehydrates the mud and then enters the pile shed.
Related Products
undefined
GUOTE MINING
Your reliable supplier
Mine Purification Equipment Engineering Laboratory. The company's products have passed ISO9001 quality system certification, environmental management system certification, occupational health and safety management system certification, EU ce certification, and dozens of national patents. Products are exported to South Korea, India, Southeast Asia, Africa and other countries and regions.
Get A Quote
If you have any questions, please feel free to leave us a message at any time



